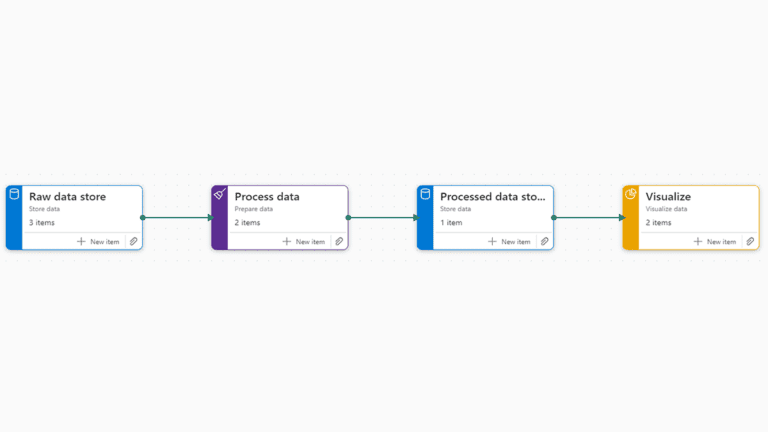
In the dynamic landscape of modern technology, businesses are navigating an unprecedented influx of data. Concurrently, advancements in computing power and storage technologies are driving costs down and efficiency up. This confluence of factors has brought about a paradigm shift that can be encapsulated in a singular, profound observation: data is eating software. This phrase reflects the growing influence of data on the development, deployment, and utility of software, signaling a transformative era in the tech industry.
The Proliferation of Data
The Exponential Growth
Data is being generated at an exponential rate. From social media interactions and IoT devices to enterprise-level transactions and user-generated content, the volume of data is expanding rapidly. IDC predicts that by 2025, the global data sphere will grow to 175 zettabytes, up from 33 zettabytes in 2018. This explosion of data is not just limited to its volume but also its variety, velocity, and veracity, creating complex challenges and opportunities for businesses.
The Shift in Business Dynamics
For businesses, this data deluge translates into both an opportunity and a necessity. Organizations that can effectively harness this data can gain valuable insights, drive innovation, and maintain a competitive edge. However, the sheer volume of data also poses significant challenges in terms of storage, management, and analysis. It necessitates advanced solutions that can scale efficiently while ensuring data integrity and security.
The Evolution of Compute and Storage
Decreasing Costs and Increasing Power
Parallel to the growth in data is the advancement in compute and storage technologies. Moore’s Law, which predicted the doubling of transistors on a microchip approximately every two years, has been a driving force behind the increase in computing power. Today, this trend is evident in the widespread availability of high-performance computing resources at a fraction of their historical costs.
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses access and utilize these resources. Providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform offer scalable, on-demand compute and storage solutions, enabling businesses to handle large-scale data without significant capital investment in infrastructure.
Enhanced Capabilities
The advancements in computing power have been complemented by improvements in storage technologies. Solid-state drives (SSDs), for instance, offer faster data access times and higher reliability compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). Furthermore, innovations in data storage methods, such as distributed file systems and object storage, have enhanced the ability to manage large datasets efficiently.
The Symbiotic Relationship: Data and Software
Data-Driven Development
The proliferation of data has led to a shift from traditional software development to data-driven development. In the past, software was designed with predefined functionalities, and data was used to feed these functionalities. Today, the scenario is reversed. Data is at the core, driving the functionalities and features of the software. Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) exemplify this shift, where algorithms learn and evolve based on the data they process.
Enhancing User Experience
Modern applications leverage data to provide personalized and intuitive user experiences. Recommendation engines, predictive analytics, and natural language processing are all powered by data, enabling software to adapt and respond to individual user behaviors and preferences. This personalized interaction not only enhances user satisfaction but also drives engagement and loyalty.
Operational Efficiency
Data is also transforming the operational aspects of software. DevOps practices, which emphasize continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD), rely heavily on data to monitor, analyze, and optimize software performance. Real-time data analytics enable quick identification and resolution of issues, ensuring robust and reliable software delivery.
The Challenges and Opportunities
Data Management and Governance
With great power comes great responsibility. The increasing reliance on data necessitates robust data management and governance frameworks. Ensuring data quality, privacy, and security are paramount concerns. Regulatory compliances, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), add an additional layer of complexity, requiring businesses to adopt stringent data handling practices.
Skill Set Evolution
The shift towards data-centricity demands a new set of skills and expertise. Data scientists, analysts, and engineers are becoming integral to software development teams. Understanding data structures, statistical analysis, and machine learning models are now crucial competencies. Continuous learning and adaptation are essential as technologies and methodologies evolve rapidly.
Strategic Innovation
Organizations that embrace the synergy between data and software stand to gain significant advantages. Data-driven insights can uncover new market opportunities, drive product innovation, and optimize operational efficiencies. Companies like Netflix, Amazon, and Google have demonstrated the transformative potential of leveraging data to inform strategic decisions and enhance customer experiences.
In the modern technological landscape, the interplay between data and software is redefining the boundaries of innovation and efficiency. The growing abundance of data, coupled with advancements in compute and storage technologies, is ushering in an era where data is no longer just a byproduct of software but the driving force behind it. Businesses that recognize and adapt to this shift are poised to thrive, leveraging data to unlock new possibilities and shape the future of technology. As we move forward, the mantra “data is eating software” will continue to underscore the pivotal role of data in the evolving digital ecosystem.